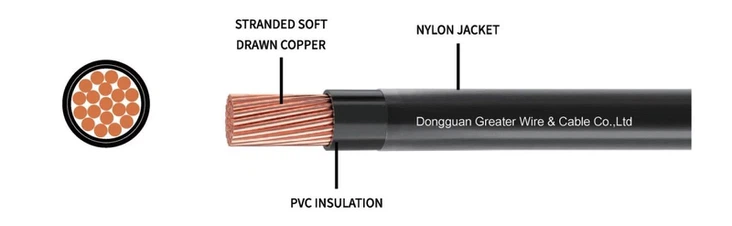
1. Basic Specifications of 6 awg thhn wire
THHN wire is a wire with a copper conductor and a thermoplastic polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and nylon protective layer. Its main features include:
Heat resistance: THHN cable can withstand an ambient temperature of 90°C (in a dry environment) and 75°C in a wet environment.
Chemical resistance: THHN wire has good chemical corrosion resistance and can prevent damage to the cable to a certain extent by oil, acid or water.
Abrasion resistance: The outer nylon layer provides a certain degree of wear protection.
6 awg thhn cable usually means that its conductor diameter is 6 AWG. In the standard electrical specifications of the United States, the rated current capacity of 6 awg thhn cable is about 55 amps, provided that it is a copper conductor cable and the installation conditions meet the relevant requirements.
2. Basic reference value of current carrying capacity
According to the standards in the National Electrical Code (NEC), the typical current carrying capacity of thhn awg 6 copper conductor is about 55 amps. However, this value is not fixed and it will be affected by many factors.
2.1 Ambient Temperature
The current carrying capacity of wire thhn is based on the measured value at a standard ambient temperature (usually 30°C or 86°F). If the ambient temperature of the cable is higher, the current carrying capacity of the conductor will decrease. For example:
At 40°C (104°F), the current carrying capacity will decrease by about 10%.
If the ambient temperature exceeds 50°C (122°F), the current carrying capacity may decrease further. The specific reduction needs to refer to the detailed specifications of the thhn cable manufacturer.
2.2 Cable Laying Method
Different installation methods will also affect the current carrying capacity of the thhn cable. If the cable is in a closed pipe or multiple cables are crowded together, the heat dissipation conditions will be affected and the current carrying capacity will be reduced. The following are several common laying methods and their effects:
Laying in open air: The current carrying capacity is higher and can usually carry the design current rating.
Laying in pipes or cable troughs: Due to limited heat dissipation, the current carrying capacity may need to be modified to a certain extent, usually reduced by 10%-20%.
Underground laying: When laying underground, the heat dissipation performance of the cable thhn is poor, especially when buried deep, which will affect its current carrying capacity.
2.3 Selection of conductor materials
THHN cables generally use copper or aluminum conductors. The current carrying capacity of wire thhn copper conductors is significantly higher than that of wire thhn aluminum conductors. The current carrying capacity of aluminum conductors is generally 15%-20% less than that of copper conductors.
For example, the current carrying capacity of cable thhn 6 aluminum conductor is usually 45 amperes, while the current carrying capacity of wire thhn 6 copper conductors of the same specification is 55 amperes.
2.4 Cable length
The length of the cable also has a certain impact on the current carrying capacity. Longer cables may cause current loss due to increased resistance, so the voltage drop of the cable also needs to be taken into account. If the voltage drop is too large, it may affect the normal operation of electrical equipment, so the cable length should be selected reasonably.
3. How to choose the right awg thhn cable size?
When choosing a 6 gauge thhn wire, you first need to determine the actual load current requirements. If the load current exceeds the cable's carrying capacity, it may cause the cable to overheat, damage the insulation layer, and even cause safety accidents such as fire. Here are a few steps to help choose the appropriate cable size:
3.1 Determine the load current
First, calculate or confirm the maximum current demand of the electrical equipment, including possible starting current. For example, electrical equipment such as air conditioners require much higher current when starting than when running. In this case, you need to consider using a cable with a higher carrying capacity.
3.2 Consider the installation environment of the cable
Understand the specific environmental conditions where the cable will be laid, including temperature, humidity, laying method, etc. If the ambient temperature is high or the laying method is restricted, you may need to use a larger cable.
3.3 Consider the length of the cable
Long cable lines may cause excessive voltage drop, so you need to ensure that the voltage drop of the cable is within a reasonable range. In order to reduce voltage drop, thicker cables are usually required when transmitting current over long distances.
3.4 Refer to electrical specifications
According to local electrical specifications (NEC or local specifications), select cable specifications that meet the requirements. When selecting cables, you also need to follow electrical safety standards to ensure that the installation is compliant.

4. Common applications of 6 gauge thhn wire
6 gauge thhn wire are commonly used for medium-power power transmission and wiring. The following are some common application scenarios:
Residential and commercial electrical wiring: thhn wire 6 gauge are commonly used for lighting circuits, air conditioners, water heaters and other equipment in residential and commercial buildings.
Connection of electrical equipment: such as industrial equipment, distribution boards, switches, etc.
Power supply circuit: thhn wire 6 gauge is a common choice in situations where higher current transmission is required but high-power electrical appliances are not involved.
5. Safety and maintenance precautions
When using 6 awg thhn wire, you must ensure the following points:
Current load is not overloaded: Make sure the current load is within the rated current range of the cable.
Regularly check the cable: Regularly check the cable for wear, aging, overheating or other damage.
Proper installation: Ensure that the cables are properly laid and in compliance with relevant electrical codes, especially in environments with heavy moisture or high temperatures.
Avoid contact with water: THHN cables are not suitable for use in environments where they are exposed to water for long periods of time.