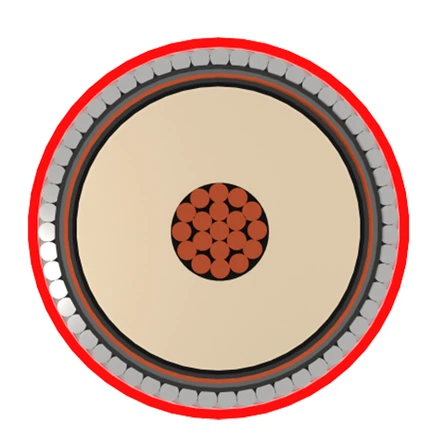
The main difference between the American standard MV 105 cable and MV 90 cable is their rated temperature. The rated temperature of the 1mV 105 cable is 105 ℃, while the rated temperature of the MV 105 cable is 90 ℃.
The rated temperature of the American standard MV 105 cable is 105 ℃, which means that the maximum temperature of the cable under long-term working conditions should not exceed 105 ℃. This type of cable typically has high heat resistance and is suitable for power transmission and distribution in high-temperature environments. The single conductor MV 105 cable has an insulation level of 133%, which improves the flexibility of the cable through a braided shielding system. It is also resistant to sunlight and oil, and has even passed the -40 ℃ cold bending test. According to NEC standards, it can be directly buried. In addition, MV 105 cables are typically used in voltage levels ranging from 5-15 kV, comply with UL2196 standards, and have FT4/IEEE 1202 flame retardant ratings.
The rated temperature of MV 90 cable is 90 ℃, suitable for general industrial and environmental environments with relatively low temperatures. Medium voltage cables are usually made up of several wires or groups of wires twisted together, with each group of wires insulated from each other and twisted around a center. The entire outer surface is covered with a highly insulated layer. Due to the conversion of thermoplastic polyethylene to thermosetting cross-linked polyethylene material in medium voltage cables, their mechanical properties, thermal aging performance, and environmental stress capacity are greatly improved, and they have excellent electrical performance. Common specifications and models include MV 105 15kV cable, MV 105 5kV cable, 4160V cable, and 35kV MV cable