In the field of electrical installation, MC cable (metal sheathed cable) and BX cable (armored cable) are two common wiring options. Although they have some similarities in appearance and are both cables with metal sheaths, the two are often confused. This article will analyze their historical background, core differences, and how to choose between these two products when purchasing, to learn MC cable and BX cable from these three aspects.
If you are looking for quality MC (Metal Clad) and BX (Armored) cables, you can contact us. All of Greater Wire Manufacturer's MC and BX cables are tested and certified according to UL 1569 and UL 4 standards. These certifications guarantee that our cables meet the highest safety and performance requirements, including resistance to heat, moisture, and mechanical stress. Whether you need MC cables for industrial environments or BX cables for residential use, our products provide consistent and reliable electrical performance.

1. Historical Background and Terminology Evolution of MC Cable and BX Cable
The history of BX Cable can be traced back to the early 20th century. Originally, the name BX was proposed by General Electric in the early 20th century (around the 1900s), with "B" standing for Braided or Bonded and "X" standing for Experimental. Early versions of BX Cable used spiral steel tape as a sheath to provide basic mechanical protection. Since the spiral steel tape has a certain conductivity, early BX Cable relied on this spiral sheath as a grounding path without an independent grounding wire. Due to its simple structure and relatively low production cost, BX Cable was quickly promoted in residential and commercial buildings in North America and became a standard wiring solution.
As the electrical industry's requirements for safety and durability continued to increase, MC Cable (Metal-Clad Cable) was introduced in the mid-to-late 20th century and gradually became the first choice for modern building wiring. The naming of MC wire reflects the significant improvement in its structure. "Metal-Clad" means that it is covered with a metal sheath to provide stronger mechanical protection and electrical shielding capabilities. Unlike BX Cable, MC Cable introduces an independent grounding conductor to improve the grounding reliability and safety of the wiring system.

2. Comparison of the core differences between MC cable and BX cable
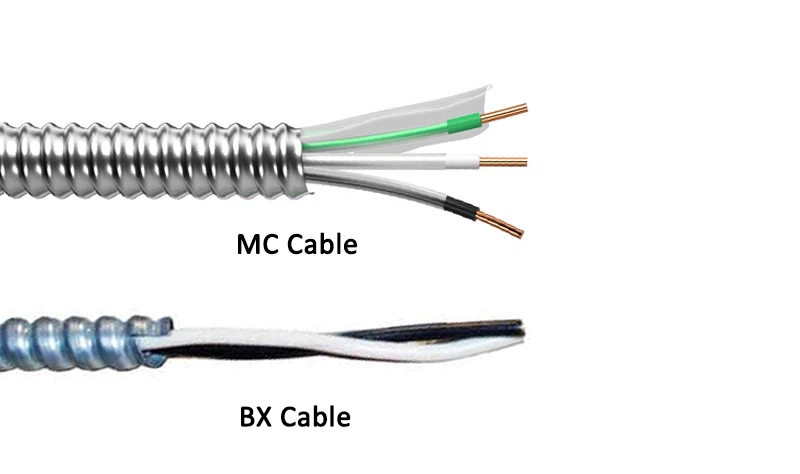
2.1 Differences in structure and materials
The outer layer of MC Cable is usually made of lightweight aluminum or galvanized steel to provide better corrosion resistance and mechanical protection. The outer layer of BX Cable is made of spirally wound steel tape, which has a tighter structure but the material itself is prone to rust in a humid environment, reducing its adaptability in complex environments.
The internal structure of MC electrical cable includes insulated conductors and independent grounding wires (usually green). Independent grounding wires improve the reliability and safety of the grounding system, ensuring the normal grounding of the system even when the armor layer is damaged. The internal structure of BX Cable usually does not include independent grounding wires but relies on the spiral steel tape itself as the grounding path. Although this design can meet basic grounding needs in short-distance wiring, in more complex electrical systems, the lack of independent grounding wires may lead to insufficient grounding performance and increase electrical safety hazards.
Fireproof plastic filling layers are usually added between the conductors of MC Cable, which not only enhances the fire resistance of the cable but also maintains the stability of the internal conductors when the cable is subjected to external pressure or bending.
BX Cable usually does not have a filling layer, which makes it easy for friction between the conductors during installation and use, which may accelerate the wear of the insulation layer and reduce the overall service life of the cable.
2.2 Differences in safety between MC cables and BX cables
MC Cable's structure and material design comply with NEC (National Electrical Code) 330.10 commercial building wiring standards and are widely used in industrial and commercial locations. In contrast, BX Cable usually does not contain a filling layer, and the internal wires are susceptible to friction and mechanical stress. It is more suitable for residential wiring specified in NEC 320.10 and should be avoided in humid or corrosive environments.
From the perspective of certification compliance, MC Cable has passed the more stringent UL 1569 certification, covering multiple tests such as moisture resistance, fire resistance, and mechanical protection to ensure its stability and safety in complex and harsh environments. BX Cable complies with the relatively early UL 4 standard, with lower requirements for safety and environmental adaptability, and is mainly used for basic electrical systems in indoor dry environments.
2.3 Different application scenarios of MC Cable and BX Cable
In building and industrial electrical wiring, MC Cable (Metal-Clad Cable) and BX Cable (Armored Cable) are suitable for different application scenarios due to their differences in structure and performance. MC Cable is mainly used in high-demand industrial and commercial environments due to its excellent protection and safety performance, while BX Cable is often used in residential and short-term projects due to its low cost and easy installation.
2.4 Differences between MC Cable (Metal-Clad Cable) and BX Cable (Armored Cable) in installation and maintenance
MC Cable's sheath is usually made of lightweight aluminum alloy or galvanized steel, where the use of aluminum makes the cable lighter and easier to bend. The higher flexibility of the aluminum sheath allows the cable to be routed in a narrow space for complex wiring operations. The sheath of BX Cable uses spirally wound steel tape. Although it performs well in mechanical protection, the weight of the steel sheath is large, and the steel tape structure makes it more rigid when bent and difficult to adjust.
2.5 Differences in maintenance costs between MC Cable (Metal-Clad Cable) and BX Cable (Armored Cable)
MC Cable's aluminum sheath has natural oxidation and corrosion resistance and can maintain good stability in humid, salt spray, or corrosive gas environments. When MC Cable is used in underground garages, bridges, tunnels, and outdoor exposure occasions, no additional anti-corrosion treatment is required, reducing long-term maintenance costs.
Although BX Cable's steel sheath performs well in physical protection, it is easy to rust or oxidize on the surface of the steel sheath in a humid or corrosive environment, resulting in reduced grounding performance or sheath damage. To prevent this, BX Cable usually needs to add an additional waterproof wrapping layer or use a special coating for protection in a humid or exposed environment. This not only increases material and labor costs but also makes maintenance more cumbersome.

3. How to choose MC Cable and BX Cable?
MC Cable is a more suitable choice when the project involves stricter safety standards and more complex environmental conditions. In the case of humid or corrosive environments, MC Cable's aluminum or galvanized steel sheath has excellent corrosion resistance and can be used for a long time in underground, bridges, tunnels, and outdoor environments without being affected by rust. In places with high fire protection requirements, MC Cable can be equipped with an optional fire-resistant plastic filling layer, which has stronger flame retardant properties and meets the fire safety requirements in industrial and commercial buildings. For large commercial or industrial projects, in commercial buildings, or industrial equipment installations involving large amounts of power transmission and complex wiring, MC Cable's flexibility and higher safety standards make it the preferred option.
BX Cable is simpler in structure and lower in cost, so it is suitable for residential and temporary power wiring occasions with relatively low safety and durability requirements. BX Cable meets the early UL 4 standard, but it lacks an independent grounding wire and fireproof filling layer, which is suitable for dry indoor environments. BX Cable is prone to rust in humid environments and is more suitable for wiring in dry walls, floors, and ceilings.
MC Cable and BX Cable produced by Greater Wire Manufacturer have passed the strict UL certification. Choosing UL-certified cables from Greater Wire will give you higher security and more stable power transmission solutions. Contact us now to get technical parameters and ordering details!























