THHN wire, short for Thermoplastic High Heat-resistant Nylon-coated wire, is one of the most versatile electrical cables in the market. Its unique construction features a durable nylon coating that enhances the wire's performance in various applications. But what exactly does this nylon coating do? In this article, we'll explore the specific roles and benefits of the nylon coating in THHN wire, or wire THHN, and its importance in ensuring safety, efficiency, and durability in electrical systems.
Construction of THHN Wire
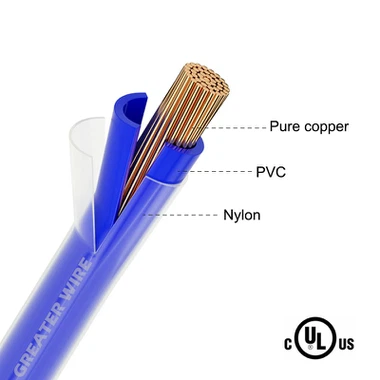
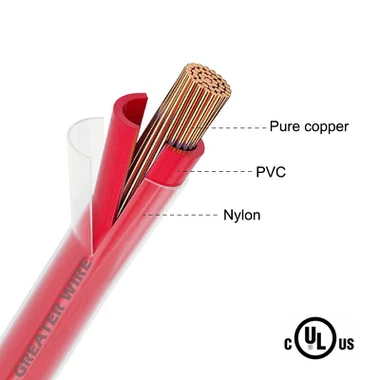
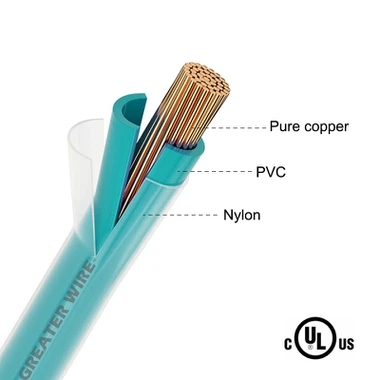
To appreciate the role of the nylon coating, it is essential to understand the overall construction of THHN wire. The cable consists of three primary layers:
Conductor: Made of copper or aluminum, providing excellent conductivity.
Thermoplastic Insulation: A heat-resistant layer that protects the conductor from electrical shorts and heat damage.
Nylon Jacket: The outermost protective layer, enhancing the cable's resilience to physical, chemical, and environmental challenges.
The Primary Roles of Nylon Coating in THHN Wire
The nylon jacket is a defining feature of THHN wire, contributing to its functionality in the following ways:
1. Abrasion Resistance
The nylon coating provides superior resistance to abrasions compared to wires without this feature.
It protects the underlying thermoplastic insulation from damage caused by pulling the wire through conduits, bending, or exposure to rough surfaces during installation.
2. Chemical Resistance
The nylon layer is resistant to many chemicals, oils, and greases commonly encountered in industrial and commercial environments.
This resistance ensures the wire's longevity and reduces the risk of insulation breakdown due to chemical exposure.
3. Moisture Resistance
While THHN wire is primarily designed for dry and damp locations, the nylon coating offers additional protection against moisture.
It prevents water ingress, reducing the likelihood of electrical shorts or degradation of the insulation layer.
4. Improved Durability in Harsh Environments
The nylon jacket protects the wire from environmental stressors such as UV radiation, minor impacts, and general wear and tear.
This durability makes wire THHN suitable for applications in commercial and industrial settings where conditions can be demanding.
Benefits of Nylon Coating for Specific Applications
1. Ease of Installation
The nylon coating reduces friction when the wire is pulled through conduits, making installation faster and easier.
Its smooth surface ensures that the insulation remains intact during this process, minimizing the risk of damage.
2. Increased Safety
The nylon layer adds an extra barrier between the conductor and the external environment, reducing the risk of electrical hazards such as arcing or shorts.
3. Extended Lifespan
By protecting the thermoplastic insulation from mechanical and chemical damage, the nylon coating increases the overall lifespan of the wire.
This makes THHN wire a cost-effective choice in long-term installations.
Applications Benefiting from Nylon Coating
The nylon coating of THHN wire makes it particularly well-suited for:
Residential Wiring
Indoor electrical systems where the wire may encounter friction during installation in conduits.
Wiring for lighting, outlets, and appliances.
Commercial Systems
Power distribution systems in offices and retail spaces where exposure to oils or greases is possible.
Industrial Applications
Environments with heavy machinery where abrasion, chemicals, and impacts are common.
Electrical systems in factories and warehouses.
HVAC Systems
High-temperature areas where resistance to heat and abrasion is critical.
Limitations of Nylon Coating
While the nylon coating offers numerous advantages, it is essential to note its limitations:
Not Suitable for Prolonged Wet Exposure
THHN wire, even with a nylon coating, is not intended for continuous exposure to wet environments.
For such applications, THWN or THWN-2 wires, which include water-resistant ratings, should be used.
Susceptibility to UV Degradation
Extended exposure to direct sunlight can degrade the nylon coating over time, making it less effective in outdoor, uncovered installations.
Proper conduit installation is recommended for outdoor use.
Temperature Sensitivity
The nylon layer adds some resistance to heat, but it is not a substitute for the heat resistance provided by the thermoplastic insulation.
Comparison of Nylon-Coated Wires
THHN vs. Non-Nylon Coated Wires
THHN Wire: Includes a nylon jacket for added durability, making it suitable for industrial and commercial use.
Non-Nylon Coated Wires: Lack the added protection, leading to reduced performance in abrasive or chemically active environments.
THHN vs. THWN-2
Both types have nylon coatings, but THWN-2 wires are explicitly rated for wet environments, offering greater versatility.
When moisture resistance is critical, THWN-2 should be chosen over standard THHN wire.
How to Maximize the Benefits of Nylon-Coated THHN Wire
Use in Conduits
Install THHN wire in properly sealed conduits to protect the nylon jacket from UV exposure and prolonged wet conditions.
Regular Inspections
Periodically check the wiring system for signs of damage to the nylon jacket, especially in high-friction or chemically active areas.
Follow Installation Guidelines
Adhere to manufacturer recommendations and local electrical codes to ensure safe and efficient use of THHN wire.